[ad_1]
Ardent Mac users claim they never would use a Windows PC. This article is not for them. It’s for the Mac users who either need to use PCs for their work or have some curiosity about what’s going on in the other camp—particularly with the arrival of new Windows 10 features and intriguing hardware like the Surface line, from the massive Studio down to the Surface Go. Switching from one OS to another always involves adjustments; our tips are intended to smooth your transition.
aybe you’ve only ever used MacBooks and iMacs but are fascinated by the vast selection of Windows computer formats, including ultraportables like the LG Gram, a full-size laptop that weighs just 2 pounds, or convertibles that do double duty as tablets and laptops. Another option comprises super high-powered gaming rigs, which you can build by yourself with hand-chosen, upgradeable parts, including a choice of AMD, Intel, processors (You can also choose an ARM-based PC in a prebuilt model). If you want a teeny tiny computer, you can choose from a selection of mini PCs, some less than half the size (and price) of Apple’s smallest option, the Mac mini. You can even get a USB stick that’s actually a PC you can plug into the back of an HDTV, such as the Lenovo Ideacentre Stick 300.
Maybe you’re intrigued by Windows 10 capabilities like touch-screen support, face-login, VR support, and accessibility features(Opens in a new window). Or maybe it’s the more extensive library of software you can run on it, including PC games not available or less full-featured on the Mac. Perhaps you’re an Android user and like the ability to see texts and photos from your phone using Windows 10’s Your Phone app.
Maybe you’re starting a new job in an office that uses Windows PCs, and learning Microsoft’s OS is less a matter of choice than necessity.
I’ve used both operating systems for years, and I appreciate both, though I find the Windows interface more flexible and efficient to work in. I will admit that macOS is somewhat easier to maintain and more trouble-free than Windows. It’s a trade-off, as my feature-by-feature comparison of macOS and Windows shows.
So, if you decide to take the plunge from Cupertino to Redmond, here are a few tips to get you started and to smooth your journey into the land of Windows 10. And once you’ve become acclimated to Windows, check out our more-advanced Hidden Tricks Inside Windows 10.
1. The Menu Is in the App

This, along with Finder-vs.-File Explorer (see next section), is perhaps the biggest paradigm difference Mac users will encounter. I’ve had Apple-centric friends tell me it’s hard to see where the menu is when they’re working in Photoshop or Word. For me, it’s more natural for the app menu to be in the app, rather than part of the operating system. You don’t need to look as far from what you’re doing. It’s just a design choice, but it’s one that I approve of.
2. Get to Know Finder’s Cousin, File Explorer

File Explorer is just what it sounds like: A window on all the files and folders on your PC. It’s similar to the Finder in macOS, though you’re less likely to use it to work with applications. The left side panel shows your folders and drives, and the right side shows their contents. You can expand and collapse subfolders in this panel, showing where in the folder structure a particular item exists. The right side of the window can show a preview or details about the currently selected item; for example, you can see a small version of a photo or document text here.
You have several view choices for the central panel: Details, List, Content, and small to extra-large icons. I prefer the details view, since it lets you sort items by name, date, size, and more. There’s no column view, and File Explorer windows aren’t tabbed, so you’ll just have to open multiple windows to see the contents of multiple folders.
Atop Explorer is a toolbar, or ribbon, with icons for common tasks like creating a new folder, moving and deleting, and renaming. You can collapse the ribbon if you find it adds clutter. The ribbon has Home, Share, View and custom tabs for things like images or compressed folders.
One of my favorite features is Quick Access, similar to the Recents view in macOS, but Quick Access shows frequent-and-recent folders at the top and recent files at the bottom. With this feature, you almost never have to worry about where you saved a file. There are set library top folders for Desktop, Downloads, Documents, Pictures, and Videos, each of which can contain multiple folders from different drives and folder locations.
3. The Taskbar, Not the Dock
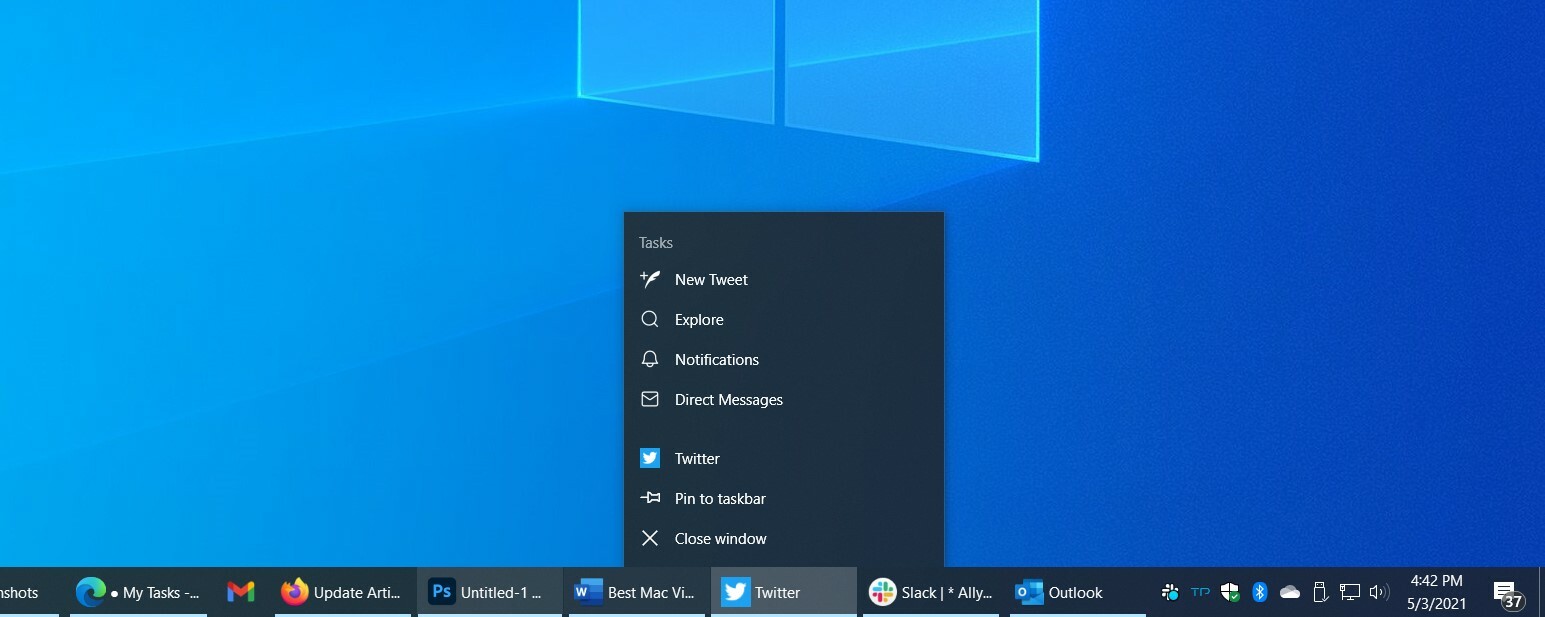
The Windows Taskbar is analogous to macOS’s Dock, but there are differences in the behavior of the two. A Taskbar entry is wide when it’s running, and pinned apps or documents are square by default; you’ll also see a bar below Taskbar entries for running apps. When you click on any Taskbar item, its window appears on the desktop and has the focus. Always. This is not always the case with the macOS Dock: I’ve often clicked an icon there to find that no program window of the clicked app appeared, sometimes prompting an expletive.
You also don’t need to worry about the stacked icons at the right side of the Dock, which behave differently from all the other Dock icons. At the right of the Taskbar is the Notification area, formerly called the System Tray. That’s analogous to the top-right notification area of macOS. It’s where you’ll see icons for services that run all the time, like online backup, VPNs, and more. Communication apps like Skype or Slack and syncing services like OneDrive, Google Drive, or online backup also use this area for small icons that show status and bring up menus upon being clicked.
System services show up here as well—think Bluetooth, security, networking, and sound. The time and date entry pops up to show your calendar schedule when clicked. The last icon to the right (with a number) is for the Action Center, for which, see the entry below.
Hovering the mouse pointer over a Taskbar item pops up thumbnails of running instances. Right-clicking shows you actions for the app, along with recent documents or webpages. You can customize the taskbar(Opens in a new window) in many ways and easily drag buttons around to change their positions.
4. Right-Click Is Your Friend
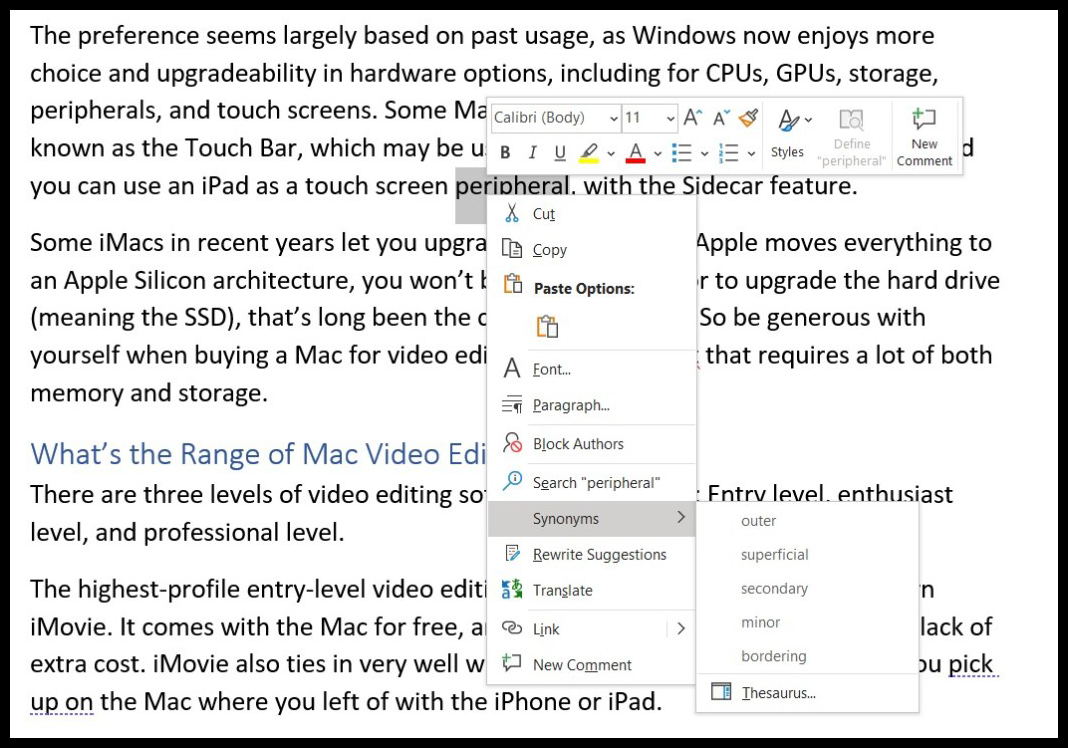
In many programs and Windows system tools, right-clicking (clicking on the right-side mouse button) gives you options and info. If you’re perplexed at something you’re seeing on the screen or want to do something with the item the cursor is over, try right-clicking. For example, in File Explorer, right-clicking on a file offers choices of opening, sharing, copying, and seeing properties of the file.
Right-clicking on an image in the Photos app lets you Add to Favorites, Delete, Rotate, Edit, Add to Album or Video, Share, Print, Save As, Resize, and so on. Photoshop offers even more right-click options. Right-click in Word, and you get quick access to font styles, highlighting, paste, synonyms, and more.
5. Minimizing, Maximizing, and Resizing Windows

One adjustment to get used to is that the window resizing buttons are at the top right of a program window, rather than the left. For some reason, I find it more natural and easy to move my mouse cursor to the top right; if I were left-handed, maybe the opposite would be true. Rather than colors, the resizing icons use symbols to indicate what they do—a bar for minimize the window to the taskbar, a rectangle for full screen, and an X to close it. Also note that closing an app with this option really closes the app; on macOS, it only closes the window, leaving the app running, possibly with no windows, which doesn’t seem useful.
The more recent Mac versions finally truly full-screen an app when you hit the green button, while Windows’ maximize button has done that forever. A difference on the Mac is that whenever you full-screen an app, it creates a virtual desktop for the maximized app, which can be a bit mind-bending. On Windows, it’s just a window that’s the full size of the screen; nothing else changes. (See below for more on virtual desktops in Windows.)
6. Installing and Uninstalling Apps

Both macOS and Windows have multiple ways of installing programs, but with Windows you never have to drag an install disk image onto a system folder. You just run a downloaded installer or choose Install on the app’s page on the Microsoft Store. Some macOS apps use PKG files rather than DMGs for a more-straightforward installation process.
Like the Mac App Store, the Microsoft Store vets software, handles updates automatically, and lets you use a purchased program on multiple machines. Unfortunately, users and developers alike haven’t really bought into the stores on desktop the way they have on mobile, so you’re more likely to find software to download on the web. To uninstall a program (whether it’s from the store or downloaded), head to Settings > Apps & Features, where you can list all installed applications by alphabetical, size, or date-installed order.
7. The Start Menu
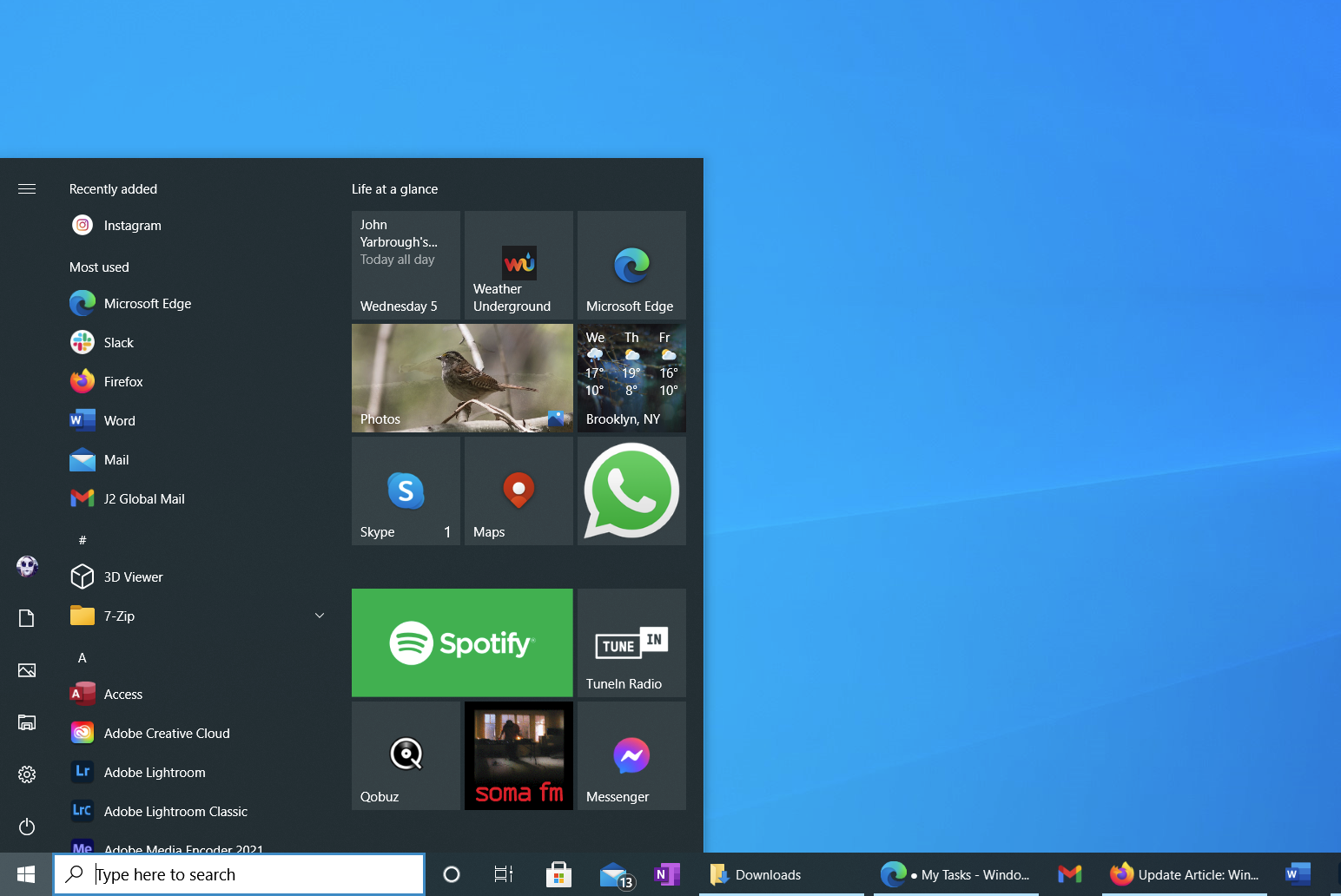
Yes, you go to the Start button to shut down your PC, to see all your applications, to get to Settings, and to open folders. Unlike the Mac’s separation of system actions and settings, everything starts from the Start menu—Mac users will be familiar with the Apple menu at the top being separate from where you start apps and access folders.
Windows 10 Start menu’s Live tiles show you the weather, your latest email topics, and your social notifications. They’re especially convenient for touch screens, but you can click them with a mouse just as easily; setting different size tiles—bigger ones for more important apps—can be helpful to make them quicker to find, too.
8. Action Center
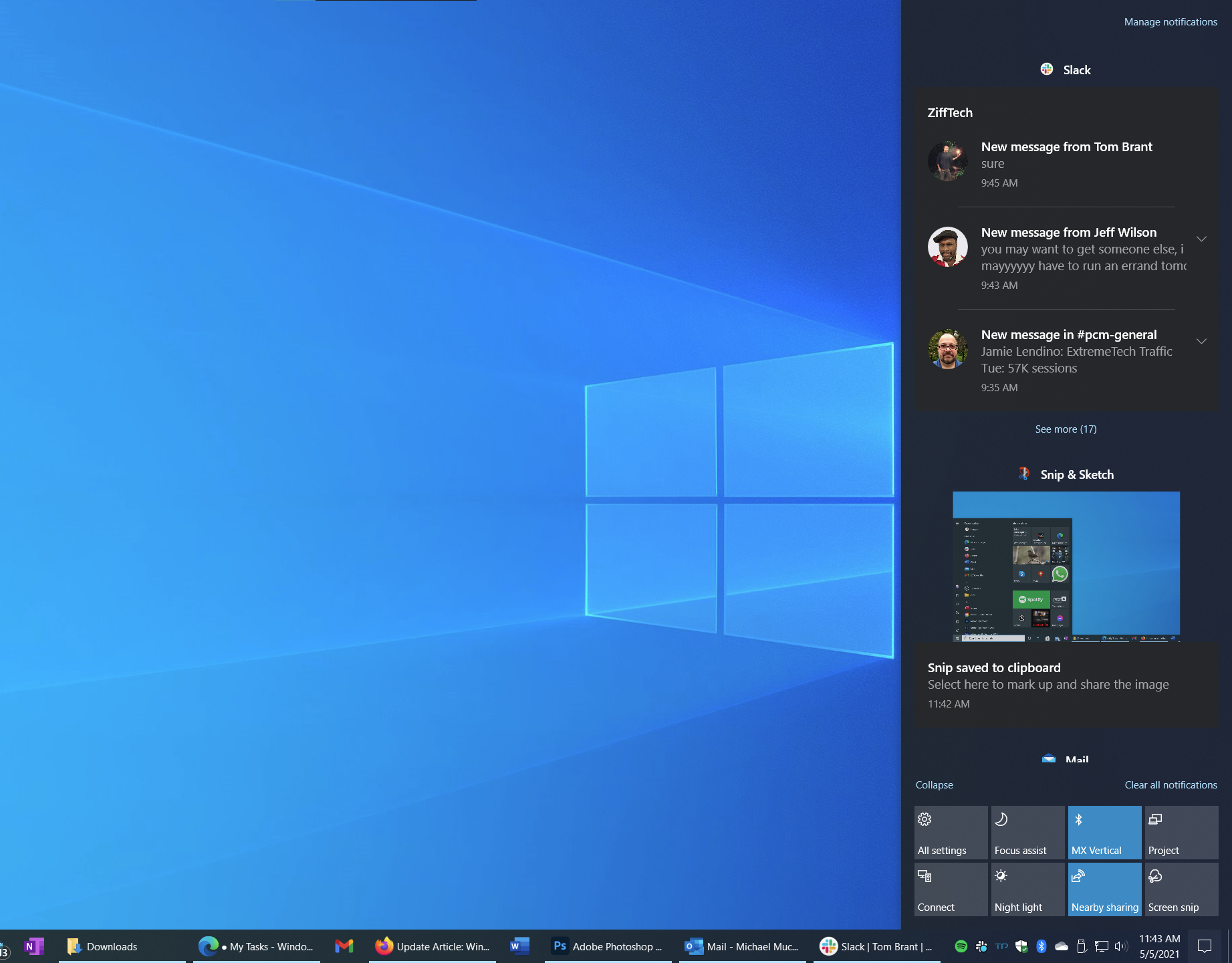
Action Center is similar to macOS’s Notifications panel. You slide out Action Center by tapping the lower-rightmost icon on the Taskbar, or, on a touch screen, by swiping in from the right. In addition to showing recent emails, news, and app notifications, Action Center’s Quick Actions buttons at the bottom let you adjust screen brightness, turn on Wi-Fi, and set other system options.
If you want some focus time, Tapping Focus assist in the Action Center silences notifications. You can also turn on Night light, which reduces blue light for late night computing.
9. Search Box

In Windows, the search box is always there, just to the right of the Start button, for you to start typing in; no need to know a keyboard shortcut or click an icon. The updated search feature proposes recent apps and documents to open, but also lets you search the web along with stuff on your own PC. Clicking the microphone icon lets you talk to Cortana for searching or app opening, saving you some typing. You can also search by image using the integrated screenshot clipping tool.
10. Task View
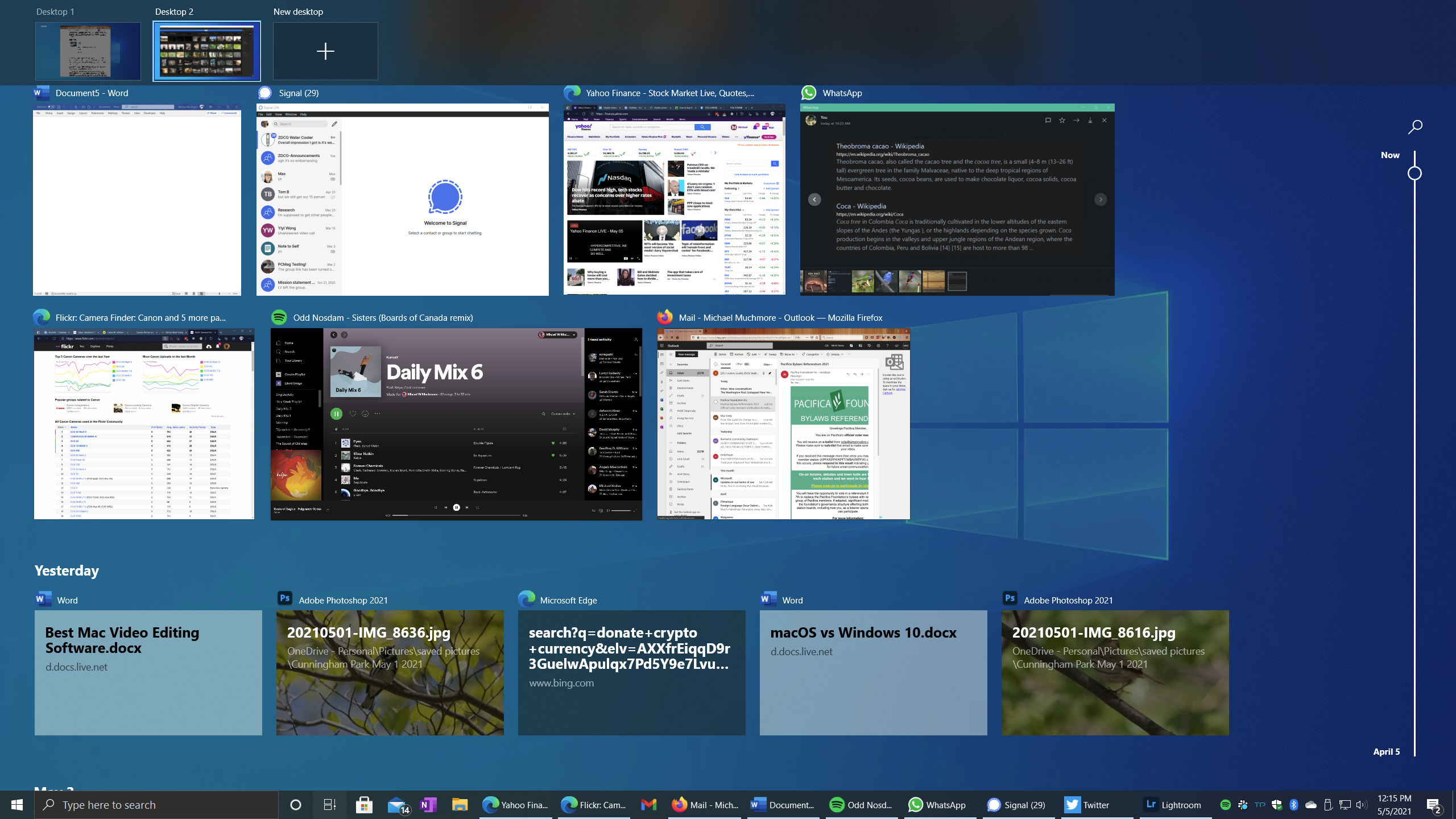
Windows was late to the party with virtual desktops, which didn’t arrive as a standard feature until Windows 10’s 2015 launch. I find them incredibly useful, and the feature is easily accessible from the Task View. You get to that view by tapping the little filmstrip icon to the right of the search bar, by swiping in from the left on a touch screen, or by tapping Windows Key–Tab. If you use the Mac’s Mission Control, this Task View will be somewhat familiar. The only added feature is the Timeline, in the bottom section of the view. At the top are your virtual desktop controls. In the middle are big tiles for currently running apps.
Adding a new virtual desktop is completely intuitive in this view, using the New Desktop choice with the big plus sign. Switching among desktops is a snap with Ctrl–Windows Key–Right Arrow or Left Arrow. I like to put my personal apps such as music and messaging in the second virtual desktop and my main work apps in the left, or first desktop.
Now, about that Timeline. If you opt in, Windows can keep track of your sites visited and documents worked on and make it easy to get back to a task. Timeline keeps a month’s worth of activity. If you use Chrome or Firefox, you can install an extension that will add activity from those browsers to the Timeline. Activities from private browsing are not included in Timeline. Microsoft is removing the option to sync your Timeline via the cloud between your home and work PC; now it’s just on the local machine.
11. Tablet Mode for Touch Screen Convertible PCs

Macs don’t have a tablet mode, since the operating system is restricted to computer use, and you need to switch to iOS (or iPadOS) to use the ecosystem’s tablets. Windows 10 gives you the option to switch to a touch-centric tablet mode for convertible PCs. That mode still allows the use of a mouse and keyboard. In Tablet mode, the Start screen tiles take up the full screen, as do running apps. Swiping down from the top all the way to the bottom conveniently closes the full-screen app. In either mode, you can swipe in from the left to see Task view and from the right to see Action Center.
12. Screen Capture
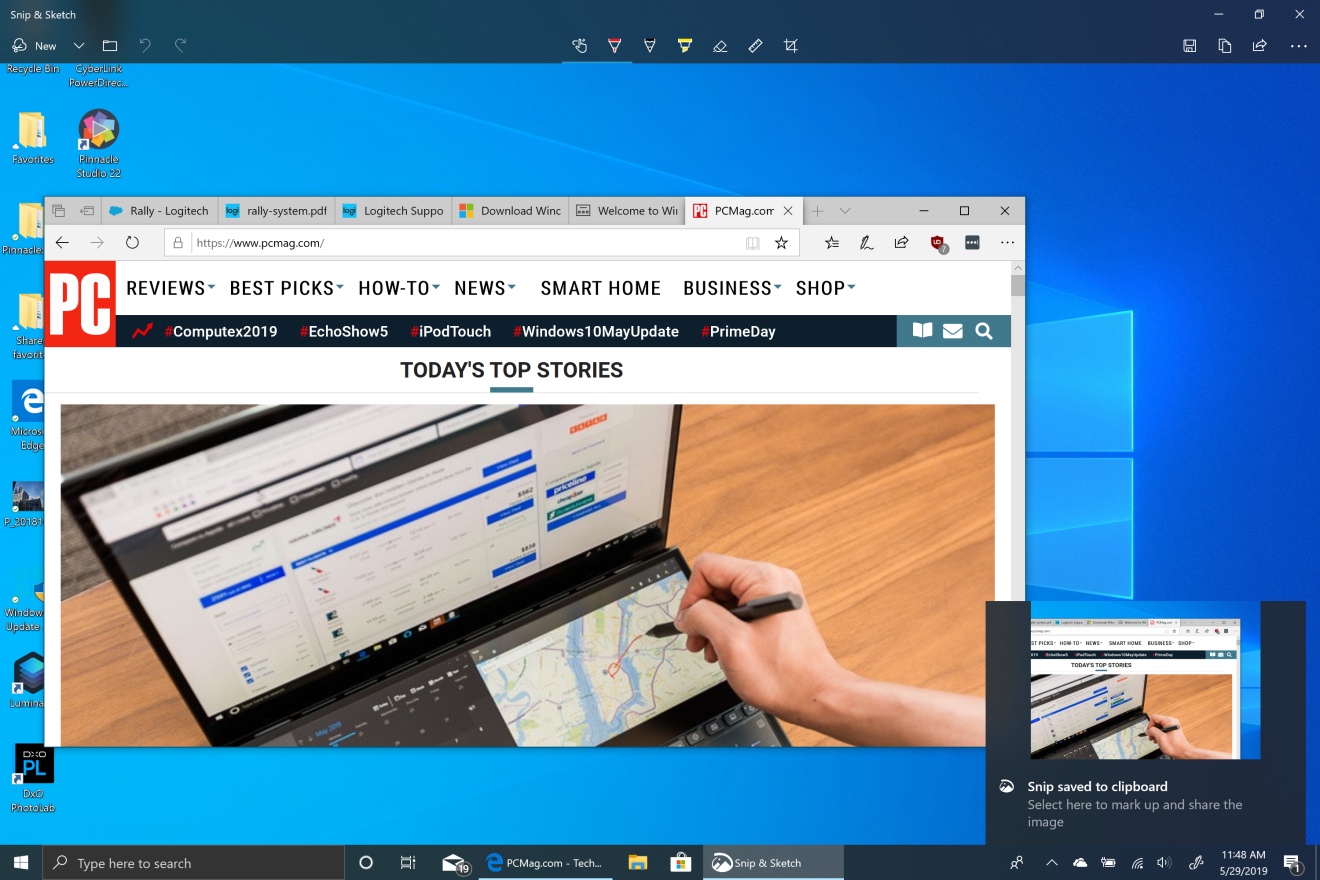
Windows has finally caught up with the Mac’s convenient screen capturing capabilities. The most full-featured way to snap a screen is by hitting Windows Key-Shift-S. This dims the screen and lets you draw a rectangle for your screenshot, shoot the current window, or the full screen. You then get a notification with a large thumbnail of the shot, which you can tap to open the Snip & Share utility. This lets you crop, mark up, and save the image to disk. It also lets you share it to any store app in the share panel that accepts images, such as Instagram, Messenger, Skype, Twitter, and email.
You can still use good-old PrtSc (or on some keyboards Print Screen) to capture the screen to the clipboard and then paste it into an image-editing app. But an even cooler option is to have the output automatically saved to a OneDrive cloud folder of your choice. If you have this option enabled in OneDrive, you see a notification in Action Center telling you that the screenshot was saved; click on the notification be taken right to the folder where the screenshot is.
13. Snapping Windows Into Place
One of Windows’ strengths is, well, windowing. You can arrange program windows literally with a snap. Just drag a window’s title bar all the way onto either side of the screen and it snaps to occupy exactly half the screen. Drag it into a corner to have the windows take up an exact quarter of the screen. If you snap one app to one side and another to the other side, you can drag the barrier between them to resize each to taste, while still using your entire screen.
To show the desktop, you can click in the extreme bottom right corner. To have a window stay the same width but maximize vertically, double click with the cursor right over the top or bottom edge of the window. And one of my faves: To hide all other windows except the one you’re working in, grab the title bar with the cursor and shake your mouse.
14. Learn the Essential Keyboard Shortcuts
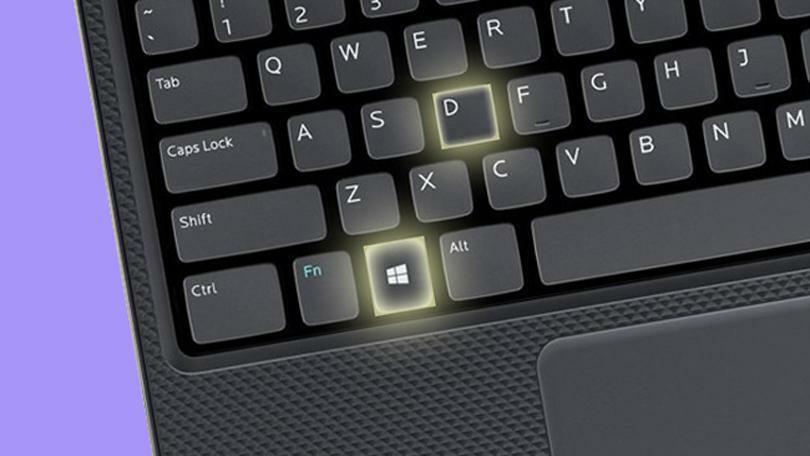

Even though Macs now, too, have a Control key, on Windows, their use is more prevalent. For example, Ctrl-C and Ctrl-V are the always-useful copy and paste key combos. Other oft-needed shortcuts include Alt-Tab to switch between running apps. Ctrl-F will open a search feature in most apps; Ctrl-Z is for undo, Ctrl-Y for redo. The PrtScn or Print Screen key does what it sounds like: Captures a screenshot. To see processes and performance, hit Ctrl-Shift-Esc, which opens the Task Manager (from there you can kill a nonresponding app, similar to the Mac’s Force Quit). For a fuller list of available shortcuts, check out our Essential Windows Shortcuts.
15. Use Cortana and Dictation
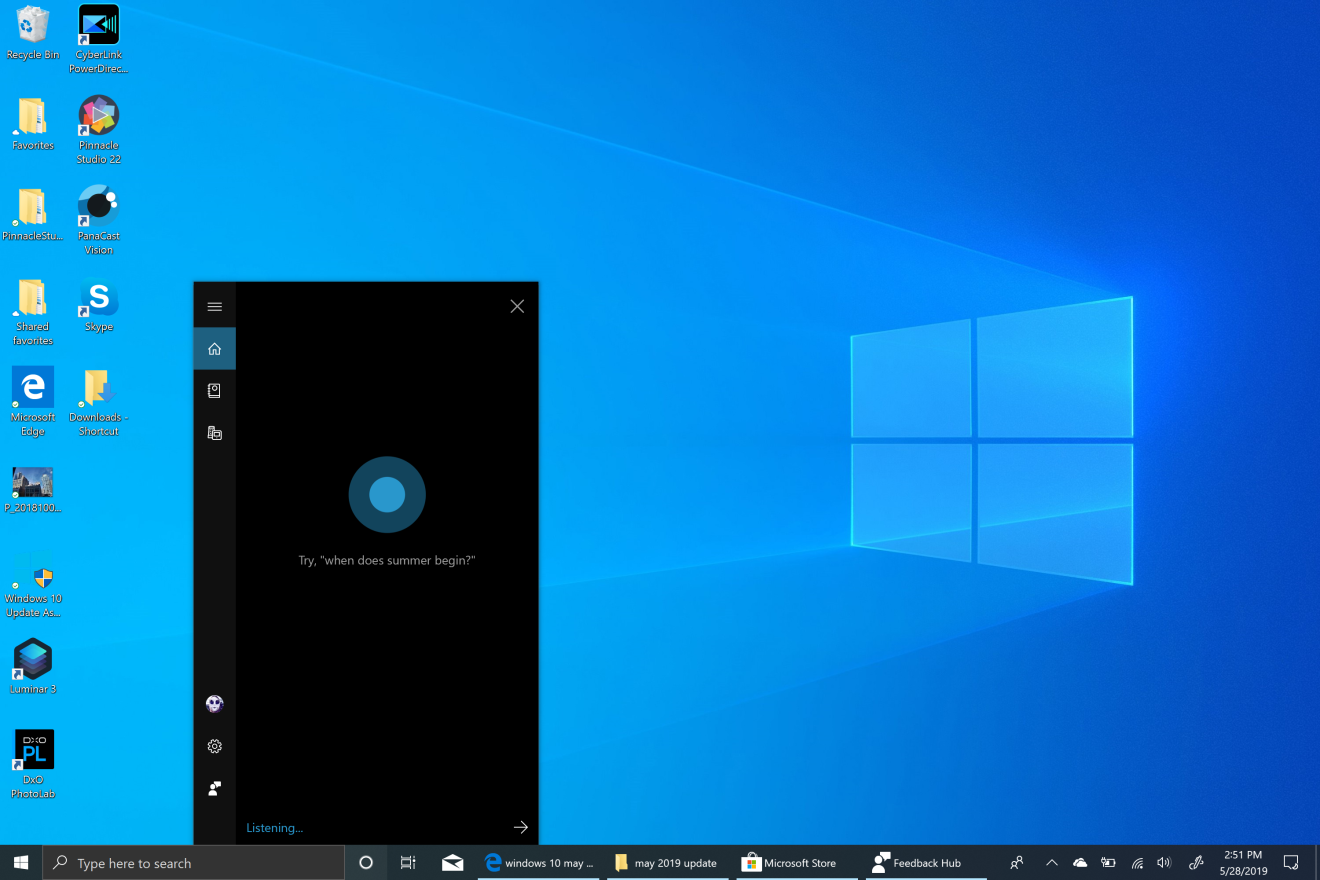
Especially if you’re on a desktop. You can open apps, navigate to websites, check the weather, get sports results, look up factual info. With our fingers constantly at risk of carpal tunnel syndrome, who wouldn’t welcome a way to save them from unnecessary keystrokes? Siri has arrived on the Mac finally, and can do a lot for you via voice, but I find it seldom can do what I ask for.
Not part of Cortana but extremely useful for saving your fingers is the dictation feature, which you can open from anywhere you’d normally have to type. Open it with the Windows Key–H shortcut. It’s a lot more accurate than these tools were in the past.
Apple macOS or Microsoft Windows 10?

For a feature-by-feature comparison between the two market-leading desktop operating systems, read our feature, macOS vs. Windows: Which OS Really Is the Best?
[ad_2]
Source link : https://www.pcmag.com/how-to/windows-10-tips-for-mac-users









